Babylonian Talmud
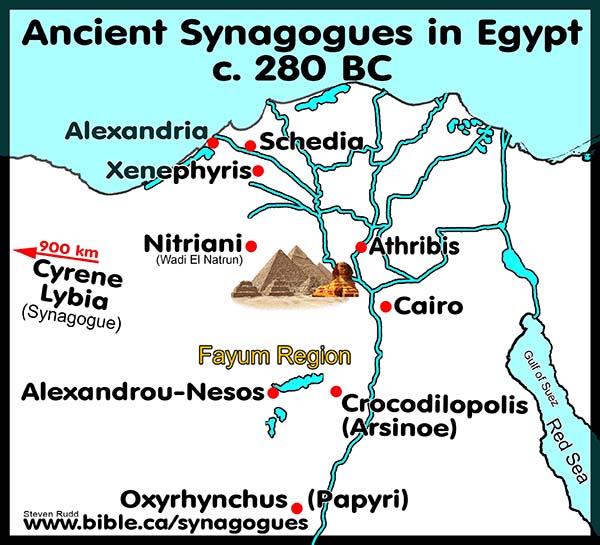
Ancient Synagogue Literary Sources
Ancient and current Non-Biblical Jewish Law
500 AD
"It was for freedom that Christ set us free; therefore keep standing firm [as Christians] and do not be subject again to a yoke of slavery." (Galatians 5:1)
“thus invalidating the word of God by your tradition which you have handed down; and you do many things such as that." (Mark 7:13)
"“Why do Your disciples break the tradition of the elders? For they do not wash their hands when they eat bread.” And He answered and said to them, “Why do you yourselves transgress the commandment of God for the sake of your tradition?" (Matthew 15:2–3)
"Then the disciples came and said to Jesus, “Do You know that the Pharisees were offended when they heard this statement?” But He answered and said, “Every plant which My heavenly Father did not plant shall be uprooted. “Let them alone; they are blind guides of the blind. And if a blind man guides a blind man, both will fall into a pit.”" (Matthew 15:12–14)
394 Synagogues, courts and schools in Jerusalem at the time of Jesus
“Three judges of civil law were in Jerusalem, Admon, Hanan, and Nahum. Said R. Pappa, “Who is the Tannaite authority who repeats, ‘Nahum’? It is R. Nathan, in accord with that which has been taught on Tannaite authority: R. Nathan says, ‘Also Nahum the Mede was among those who make decrees in Jerusalem,’ but sages did not concur with him.” And were there no others? Didn’t R. Phineas say R. Oshayya said, “There were three hundred ninety-four courts in Jerusalem, corresponding to the number of synagogues and the number of schoolhouses and the number of schools for scribes”? There were many more, to be sure, but we make reference in particular to judges of civil law. Said R. Judah said R. Assi, “The civil judges who were in Jerusalem would collect their salary of ninety-nine maneh from Temple funds. If they didn’t find that suitable, they would add to the salary.” “If they didn’t find that suitable”? So are we dealing with money grubbers? Rather: “If they didn’t find that sufficient,” they would give them more, even though they didn’t want it.” (Babylonian Talmud, b. Ketub. 13:1, I.2.A–3.C)
History and content of the Babylonian Talmud:
1. “The editing of the Babylonian Talmud has received a good deal of scholarly attention, most of which Neusner (1970) and Goodblatt (1979: 291–318) have summarized. The traditional view, based on a few ambiguous passages from the Babylonian Gemara, a letter of Sherira ben Hanina Gaon of Pumbedita (ca. 906–1006 c.e.), and a comment by Rabbi Solomon ben Isaac of Provance (Rashi, 1040–1105), attributes the final editing of the Babylonian Talmud to Rav Ashi (died 427/28) and Ravina II (ca. 500). The traditional view does recognize the fact that traditions were produced after Ashi and Ravina, for even Sherira mentions R. Yose, one of the Seboraim, during whose days the Babylonian Talmud reached its ultimate conclusion (Berkovits EncJud 15: 761). (ABD, Talmud, Volume 6, Pages 313, 1992 AD)
2. “The Talmud (lit. “learning,” or what is to be “learned,” from lāmad, “to learn”) is a compendium of rabbinic law and lore that combines Mishnah and gemara (“completion”), as well as portions of the Tosefta (see Rabbinic Literature: Mishnah and Tosefta). The mishnaic material derives from the tannaitic rabbis and sages (c. 50 b.c. to a.d. 200), while the gemara derives mostly from the amoraic rabbis of a later period (c. a.d. 200–500). Included in the gemara are tannaitic sayings not included in the Mishnah. These traditions are called baraitoth (“external [sayings]”), in that they reach back to the tannaitic period but are external to the Mishnah. Although the Talmud postdates the NT by several centuries, it offers potentially useful background material.” (Dictionary of New Testament Background, Rabbinic Literature: Talmud, p897, 2000 AD)
3. “The Babylonian Talmud is considered the most important collection of texts in rabbinic literature. It spans 2,783 folio pages in the standard editions. Although the collection takes the form of commentary on the Mishnah, the ancient rabbis included discussions and rulings on nearly every subject possible. Due to its incredible scope, the Babylonian Talmud became the fundamental text of Jewish life in the Middle Ages and for many people beyond this period. The Talmud of the Land of Israel (Palestinian/Jerusalem Talmud) was edited in Israel, prior to the editing of the Babylonian Talmud. However, it is much shorter and lacks the heavy editorial work that characterizes the Babylonian Talmud; thus, the Palestinian Talmud never gained the high position that the Babylonian Talmud has. Nevertheless, both Talmuds contain material from an earlier period and are also extremely useful for illuminating the background of the New Testament and early Christianity.” (Lexham Bible Dictionary, Talmud, 2016 AD)
4. “Talmud Babli. The Babylonian Talmud was edited sometime after a.d. 500 and up to a.d. 600. As the name suggests, it was produced in Babylon, where a large Jewish population developed in the aftermath of the Babylonian capture of Jerusalem and destruction of the Jewish temple in 586 b.c. Most of the cited rabbinic authorities were from Babylon, though Palestinian authorities are also cited. Babli comments and expands upon the second, third, fourth and fifth divisions of the Mishnah, as well as part of the first division. Babli interprets and embellishes the Mishnah, exegetes Scripture, identifies anonymous authorities and discusses a variety of topics that fall outside the subject of the Mishnah. Whereas there is almost no messianic tradition in the Mishnah (see the later insertion at m. Soṭa 9:15), there is comparatively a great deal of messianic lore in Babli.” (Dictionary of New Testament Background, Rabbinic Literature: Talmud, p898, 2000 AD)
Comments:
1. The specific passage of Ketub. 13:1, I.2.A–3.C, states there were 394 synagogues and courts and schools in the first century AD in the second temple period.
2. The Babylonian Talmud is a further invention of non-Mosaic laws that Messiah, Jesus Christ condemned:
a. Some contradicted Mosaic law while others, like washing of hands, was the creation of new sin laws where God was OK with the practice.
b. "The Pharisees and some of the scribes gathered around Him when they had come from Jerusalem, and had seen that some of His disciples were eating their bread with impure hands, that is, unwashed. (For the Pharisees and all the Jews do not eat unless they carefully wash their hands, thus observing the traditions of the elders; and when they come from the market place, they do not eat unless they cleanse themselves; and there are many other things which they have received in order to observe, such as the washing of cups and pitchers and copper pots.) The Pharisees and the scribes asked Him, “Why do Your disciples not walk according to the tradition of the elders, but eat their bread with impure hands?” And He said to them, “Rightly did Isaiah prophesy of you hypocrites, as it is written: ‘This people honors Me with their lips, But their heart is far away from Me. ‘But in vain do they worship Me, Teaching as doctrines the precepts of men.’ “Neglecting the commandment of God, you hold to the tradition of men.” He was also saying to them, “You are experts at setting aside the commandment of God in order to keep your tradition. “For Moses said, ‘Honor your father and your mother’; and, ‘He who speaks evil of father or mother, is to be put to death’; but you say, ‘If a man says to his father or his mother, whatever I have that would help you is Corban (that is to say, given to God),’ you no longer permit him to do anything for his father or his mother; thus invalidating the word of God by your tradition which you have handed down; and you do many things such as that.”" (Mark 7:1–13)
c. “R. Eliezer says, “They unloose a vow for a person by [reference to] the honor of his father or mother.” B. And sages prohibit. C. Said R. Sadoq, “Before they unloose a vow for him by [reference to] the honor of his father or mother, let them unloose his vow by reference to the honor of the Omnipresent. D. “If so, there will be no vows!” E. But sages concede to R. Eliezer that, in a matter which is between him and his mother or father, they unloose his vow by [reference to] the honor of his father or mother.” (Babylonian Talmud m. Nedarim 9:1)
d. In fact, in the Babylonian Talmud, The word “qorban” is used over 100 times. So a person would vow to give all their money to the Temple when they die, meaning that none of the money could be used for helping their parents, but of course, they get to use the money until they die. Selfish and invalidating the Word of God.
e. The first century Jews took a verbal beating from Jesus because he said they were breaking the 5th commandment (honour father and mother) to keep Nedarim 5. Which #5 law was better to keep? Nedarim or the 5th commandment of Moses? The answer it obvious.
3. Many non-Mosaic rules like handwashing continues to this day in spite of Jesus’ criticism of it on a ritual purity basis:
a. "It was for freedom that Christ set us free; therefore keep standing firm and do not be subject again to a yoke of slavery." (Galatians 5:1)
b. "Then some Pharisees and scribes came to Jesus from Jerusalem and said, “Why do Your disciples break the tradition of the elders? For they do not wash their hands when they eat bread.” And He answered and said to them, “Why do you yourselves transgress the commandment of God for the sake of your tradition? “For God said, ‘Honor your father and mother,’ and, ‘He who speaks evil of father or mother is to be put to death.’ “But you say, ‘Whoever says to his father or mother, “Whatever I have that would help you has been given to God,” he is not to honor his father or his mother.’ And by this you invalidated the word of God for the sake of your tradition. “You hypocrites, rightly did Isaiah prophesy of you: ‘This people honors Me with their lips, But their heart is far away from Me. ‘But in vain do they worship Me, Teaching as doctrines the precepts of men.’ ” After Jesus called the crowd to Him, He said to them, “Hear and understand. “It is not what enters into the mouth that defiles the man, but what proceeds out of the mouth, this defiles the man.” Then the disciples came and said to Him, “Do You know that the Pharisees were offended when they heard this statement?” But He answered and said, “Every plant which My heavenly Father did not plant shall be uprooted. “Let them alone; they are blind guides of the blind. And if a blind man guides a blind man, both will fall into a pit.”" (Matthew 15:1–14)
c. "The Pharisees and some of the scribes gathered around Him when they had come from Jerusalem, and had seen that some of His disciples were eating their bread with impure hands, that is, unwashed. (For the Pharisees and all the Jews do not eat unless they carefully wash their hands, thus observing the traditions of the elders; and when they come from the market place, they do not eat unless they cleanse themselves; and there are many other things which they have received in order to observe, such as the washing of cups and pitchers and copper pots.) The Pharisees and the scribes asked Him, “Why do Your disciples not walk according to the tradition of the elders, but eat their bread with impure hands?” And He said to them, “Rightly did Isaiah prophesy of you hypocrites, as it is written: ‘This people honors Me with their lips, But their heart is far away from Me. ‘But in vain do they worship Me, Teaching as doctrines the precepts of men.’ “Neglecting the commandment of God, you hold to the tradition of men.” He was also saying to them, “You are experts at setting aside the commandment of God in order to keep your tradition. “For Moses said, ‘Honor your father and your mother’; and, ‘He who speaks evil of father or mother, is to be put to death’; but you say, ‘If a man says to his father or his mother, whatever I have that would help you is Corban (that is to say, given to God),’ you no longer permit him to do anything for his father or his mother; thus invalidating the word of God by your tradition which you have handed down; and you do many things such as that.”" (Mark 7:1–13)
d. “The “tradition of the elders” is simply the oral, scribal interpretation of the written, Mosaic law. This tradition was later (ca. a.d. 220) collected and reduced to writing in the Mishna. The “elders” were scribes, Pharisees, leaders of synagogues, and revered persons in general.” (The New American Commentary, Mark 7:3)
e. “2:3 A The hands are susceptible to uncleanness and are rendered clean up to the wrist. B How so? C [If] one poured the first [water] up to the wrist, and the second beyond the wrist and it went back to the hand—it is clean. D [If] he poured out the first and the second [pouring of water] beyond the wrist and it went back to the hand, it is unclean. E [If] he poured out the first water onto one hand, and was reminded and poured out the second [water] on to both hands, they are unclean. F [If] he poured out the first water on to both hands and was reminded and poured out the second [water] on to one hand, his hand [which has been washed twice] is clean. G [If] he poured out water on to one hand and rubbed it on the other, it is unclean. H [If he rubbed his hand] on his head or on the wall, it is clean. I They pour out [water on the hands of] four or five people side by side, or above one another, J on condition that they [the hands] lie loosely so that the water will flow among them.” (Mishnah m. Yadayim 2:3)
4. Sabbath Day’s Journey: 2000 cubits or 915 meters
a. "Then they returned to Jerusalem from the mount called Olivet, which is near Jerusalem, a Sabbath day’s journey away." (Acts 1:12)
b. “A He who went forth [beyond the Sabbath line] on a permissible mission, B but they said to him, “The deed already has been done,” C has two thousand cubits in every direction [in which to walk about]. D If he was within the Sabbath line, it is as if he never went forth. E For all those who go forth to save [someone in danger] may go back to their place.” (Mishnah m. 'Erub. 4:3)
5. There are many of these rules today in modern Israel:
a. You cannot push a button to start a kitchen appliance, so most modern appliances have “sabbath mode” which will override the safety timer on stove so it will never shut off. This allows the Jew to turn the stove on just before the sabbath and cook on the sabbath without breaking the sabbath by turning on the stove. Fridges and stoves with “sabbath mode” will not turn the lights on when you open the doors. Compressors are randomly delayed since they usually turn on when the door is opened.
b. It breaks the sabbath if you are at a hotel and you push the elevator button. So elevators are programmed for “sabbath mode” so that the continuously move from top to bottom, then bottom to top, stopping at each floor and opening the doors. This allows a Jew to get on the elevator without pushing any buttons. Since it is automatic, he is not responsible for breaking the sabbath. The machine is breaking the sabbath for him.
c. This is why El Al Airlines will not book flights on the Sabbath.
Synagogue exerts from the Jerusalem and Babylonian Talmud:
1. 480 Synagogue schools and 394 Synagogues, courts and schools in Jerusalem
a. “Three judges of civil law were in Jerusalem, Admon, Hanan, and Nahum. Said R. Pappa, “Who is the Tannaite authority who repeats, ‘Nahum’? It is R. Nathan, in accord with that which has been taught on Tannaite authority: R. Nathan says, ‘Also Nahum the Mede was among those who make decrees in Jerusalem,’ but sages did not concur with him.” And were there no others? Didn’t R. Phineas say R. Oshayya said, “There were three hundred ninety-four courts in Jerusalem, corresponding to the number of synagogues and the number of schoolhouses and the number of schools for scribes”? There were many more, to be sure, but we make reference in particular to judges of civil law. Said R. Judah said R. Assi, “The civil judges who were in Jerusalem would collect their salary of ninety-nine maneh from Temple funds. If they didn’t find that suitable, they would add to the salary.” “If they didn’t find that suitable”? So are we dealing with money grubbers? Rather: “If they didn’t find that sufficient,” they would give them more, even though they didn’t want it.” (Babylonian Talmud, b. Ketub. 13:1, I.2.A–3.C)
b. “‘The house of the Lord’ refers to the Temple. ‘And the king’s house’ refers to the palace of Zedekiah. ‘And all the houses of Jerusalem’ refers to the 480 synagogues that were in Jerusalem. For R. Phineas in the name of R. Hoshaiah: “There were 480 synagogues in Jerusalem and every one of them had a schoolhouse and a house for learning, a schoolhouse for Scripture and a house of learning for Mishnah.” (Jerusalem Talmud, y. Meg. 3:1, II.2.D–E)
2. Public readings:
a. “[I:1 A] [73d], Said R. Yohanan, “[The rule of M. 3:1A] represents the view of R. Menahem b. R. Yosé. For R. Menahem b. R. Yosé said, ‘The street of a town is subject to sanctification. For they take a scroll of the Torah out into the street and read it publicly there.’” (Jerusalem Talmud, y. Meg. 3:1, I.1.A)
b. “And Israelites who belong to that watch gather together in their towns [ie. In the synagogues in each town is generally accepted] and study the story of the works of creation.” (Mishah, m. Ta'an. 4:2 F)
3. Benevolence for poor:
a. “And said R. Eleazar, “They may pledge charity for the poor on the Sabbath.” And said R. Jacob said R. Yohanan, “They may go to synagogues and study houses to supervise public business on the Sabbath.” (Babylonian Talmud, Ketubot 5A:E-F)
4. Hostel:
a. “And from the perspective of Samuel, why recite the sanctification prayer in the synagogue? To carry out the obligation of guests, who eat, drink, and sleep in the synagogue.” (Babylonian Talmud, b. Pesah. 10:1, I.5.F–G)
5. No common meals eaten in synagogues:
a. “The rabbis taught: [Regarding] synagogues: One may not behave in a lightheaded manner in them; one may not eat in them; and one may not drink in them; and may not dress up in them; and one may not stroll in them; and one may not enter them in the [season of the] sun, because of the sun, or in the [season of the] rain, because of rain; and one may not conduct mourning in them for an individual. But one may read [i.e., the Bible] in them; and one may study [i.e., the Mishnah] in them; and one may conduct public mourning there.” (Babylonian Talmud, 1b. Meg. 4:4, I.1.A–C)
b. Strangely, when the synagogue was being used as a hostel, food could be eaten outside religious practice: “And from the perspective of Samuel, why recite the sanctification prayer in the synagogue? To carry out the obligation of guests, who eat, drink, and sleep in the synagogue.” (Babylonian Talmud, b. Pesah. 10:1, I.5.F–G)
6. Holy Ark of the scripture scrolls:
a. The most likely place would be on the wall opposite the door.
b. “He who makes an ark for a scroll and covering for a [hob] scroll” (Jerusalem Talmud, y. Meg. 3:1, II.4.C)
c. “Townsfolk who sold a street of a town may buy with its proceeds a synagogue. [If they sold] a synagogue, they may buy an ark. [If they sold] an ark, they may buy wrappings. [If they sold] wrappings, they may buy scrolls [of the prophets or writings]. [If they sold] scrolls, they may buy a Torah scroll. But if they sold a Torah scroll, they should not buy scrolls. [If they sold] scrolls, they should not buy wrappings. [If they sold] wrappings, they should not buy an ark. If they sold] an ark, they should not buy a synagogue. If they sold] a synagogue, they should not buy a street. And so with the surplus [of the proceeds of any of] these.” (Jerusalem Talmud, y. Meg. 3:1)
d. “As to these [namely, the ark for a scroll or coverings for a scroll]―if one had made them to begin with for secular purposes, and then went and consecrated them, what is the law governing them?” (Jerusalem Talmud, y. Meg. 3:1, II.4.K)
e. “A curtain which is on an ark has the status of the ark” (Jerusalem Talmud, y. Meg. 3:1, II.7.B)
f. “They bring forth the ark into the street of the town and put wood ashes on the ark, on the head of the patriarch, and on the head of the head of the court.” (Mishnah, m. Ta'an. 2:1 B)
7. Minors not permitted to read or touch the Ark of the Scrolls:
a. “He who concludes with the prophetic lection is the one who recites the Shema [with its blessings fore and aft], and passes before the ark, and raises his hands [in the priestly benediction]. But if he was a minor, his father or his teacher pass [before the ark] in his behalf. It was necessary to include the Mishnah’s rule only to indicate that the one who recites the Shema is the one who passes before the ark, and he is the one who raises his hands [since these are all part of the liturgy]. R. Yosé b. Haninah said, “It was so as to give encouragement [to the one who did all these things, assigning them all as a form of recognition to him].” But if he was a minor, his father or his teacher pass before the ark in his behalf. And lo, we have learned: A minor does not recite the Shema [M. 4:7B]. Said R. Yudan, “In this case [in which he may do so] it is when he has produced two pubic hairs, and in that case, in which he may not do so, he has not yet produced two pubic hairs.” (Jerusalem Talmud, y. Meg. 4:6)
8. Women will die young for these three sins:
a. “Our rabbis have taught on Tannaite authority: For three sins women die in childbirth. R. Eleazar says, “Women die young.” R. Aha says, “For the sin of covering up their babies’ shitty diapers on the Sabbath.” Others say, “Because they call the holy ark ‘chest.’ ” It has been taught on Tannaite authority: R. Ishmael says, “For two sins ignorant people die, because they call the holy ark ‘chest,’ and because they call a synagogue ‘a house of the people.’ ” (Babylonian Talmud, b. Shabb. 2:6, I.8.A–9.B)
9. Praying towards Jerusalem:
a. The very first synagogues did not concern themselves with facing Jerusalem. The reason is because they all sat in a circle making orientation irrelevant to reading and praying. The first Jerusalem oriented synagogues did not first appear until about 150 AD.
b. “Those who stand and pray outside the Land of Israel, turn to face the Land of Israel [to pray]. And what is the basis [in Scripture for this rule]? [8c] ‘And pray to thee toward their land which thou gavest their fathers’ [1 Kings 8:48]. [C] Those who stand and pray in the Land of Israel turn to face Jerusalem. And what is the basis [in Scripture for this rule]? ‘Toward the city which thou hast chosen’ [ibid. cf. 2 Chron. 6:34] [T. 3:15]. [D] Those who stand and pray in Jerusalem, turn to face the Temple mount. And what is the basis [in Scripture]? ‘And the house which I have built for thy name’ [ibid. cf. 2 Chron 6:32]. [E] And those who stand and pray on the Temple mount, turn to face the chamber of the Holy of Holies. And what is the basis [in Scripture for this rule]? ‘[And hearken to the supplication of thy servant and of thy people Israel,] when they pray toward this place; yea, hear thou in heaven thy dwelling place; and when thou hearest, forgive’ [1 Kings 8:30]. [F] It turns out that [when they pray] those who stand north [of the Temple], face south, those who stand in the south, face north, those who stand in the east, face west, those who stand in the west, face east. It turns out that all of Israel prays towards one place [T. 3:16]. [G] That accords with [the verse], ‘For my house shall be called a House of Prayer for all peoples’ [Isa. 56:7]. [I:4 A] Said R. Joshua b. Levi, “[We find the following phrase in a verse referring to the Temple,] ‘The house, that is, the nave in front of the inner sanctuary’ [1 Kings 6:17]―[this phrase suggests they stood during prayer in front of] the nave [of the Temple―the place] to which all people faced.” [B] This [rule that one must pray facing the Temple] applies at a time when the Temple was standing. How do we know [it applies] when the Temple is destroyed [i.e. that all must still face the Temple mount when praying]?” (Jerusalem Talmud, y. Ber. 4:6, I.3.B–4.B)
|
Ancient Jewish Literary Sources Non-Biblical, Non-Mosaic first century oral tradition codified into modern Jewish law |
|||
By Steve Rudd 2017: Contact the author for comments, input or corrections
|
Jesus your messiah is waiting for you to come home! |
|
|
Why not worship with a first century New Testament church near you, that has the same look and feel as the Jewish Synagogue in your own home town. As a Jew, you will find the transition as easy today as it was for the tens of thousands of your forefathers living in Jerusalem 2000 years ago when they believed in Jesus the Nazarene (the branch) as their messiah. It’s time to come home! |
|
By Steve Rudd: Contact the author for comments, input or corrections.
Go to: Main Ancient Synagogue Start Page